SUMMING PARAMETERS - COMPENSATION MECHANISM.
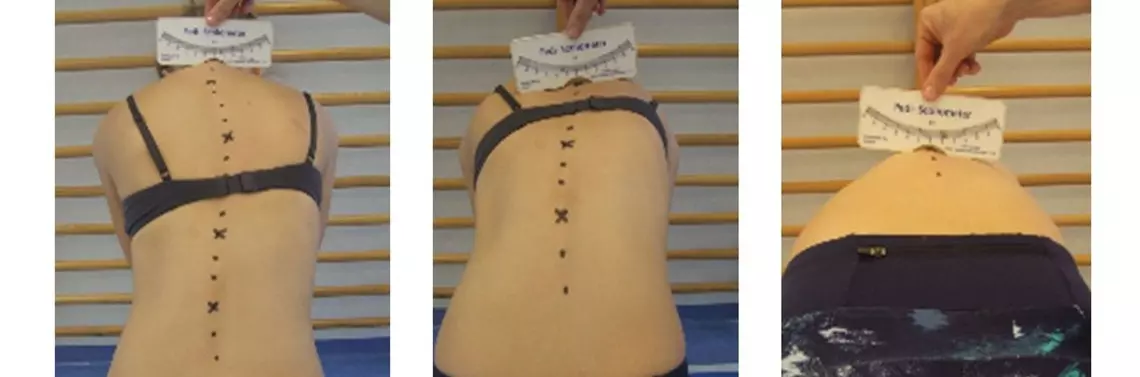
The vertebral axial rotation is a characteristic of the spine deformation in idiopathic scoliosis [8]. It is evaluated by the Adam’s test using the Bunnell’s scoliometer, which is a simple and easy to use measuring device characterised by high sensitivity and repeatability, and its availability makes it useful for screen tests [2,3,4,19]. A reduction in costal hump during treatment indicates that a three-dimensional correction was achieved, and represents an important part of the treatment result assessment by a patient [1]. The scoliometer can be used to evaluate an angle of rotation of individual arches and a global trunk rotation.
The angle of trunk rotation (ATR) is measured at a level of the scoliosis apex, both for the primary and the secondary scoliosis.

The global trunk rotation can be measured by using summing parameters. The sum of rotation (SR) represents a sum of angles of trunk rotation at a level of 12 thoracic and 5 lumbar vertebrae, with a correction for pelvis rotation. A shorter method for evaluation of the global scoliotic deformation is the Hump Sum parameter, also known as the Suzuki Hump Sum. It is...
Pozostałe 90% treści dostępne jest tylko dla Prenumeratorów
- 10 wydań czasopisma "Praktyczna Fizjoterapia i Rehabilitacja"
- Nielimitowany dostęp do całego archiwum czasopisma
- ...i wiele więcej!

Nowoczesna wiedza, którą od razu wykorzystasz w pracy z pacjentem.
Specjalistyczne czasopismo dla fizjoterapeutów, łączące aktualną wiedzę naukową z codzienną praktyką kliniczną.